General background of Yarrowia lipolytica:
Yarrowia lipolytica is a species of non-conventional and GRAS (generally regarded as
safe) yeast widely utilized in industrial applications such as organic acid and protein
production. As unicellular organism, it has the advantages of E. coli and Saccharomyces
cerevisiae in ease of manipulation and growth capacity. But, it also functions as a higher
eukaryotic organization able to perform post-translational processing of complex
proteins. As compared to S. cerevisiae, Y. lipolytica has certain advantages, such as a
mainly co-translational secretion pathway (like in mammalian cells), higher secretion
capacity and product yield, less hyperglycosylation on products, and simplicities in
scaling-up production. These features make Y. lipolytica very useful as a protein
expression system. Furthermore, the whole genome of Yarrowia lipolytica has been
sequenced; please check http://cbi.labri.fr/Genolevures/elt/YALI for details.
Product Description:
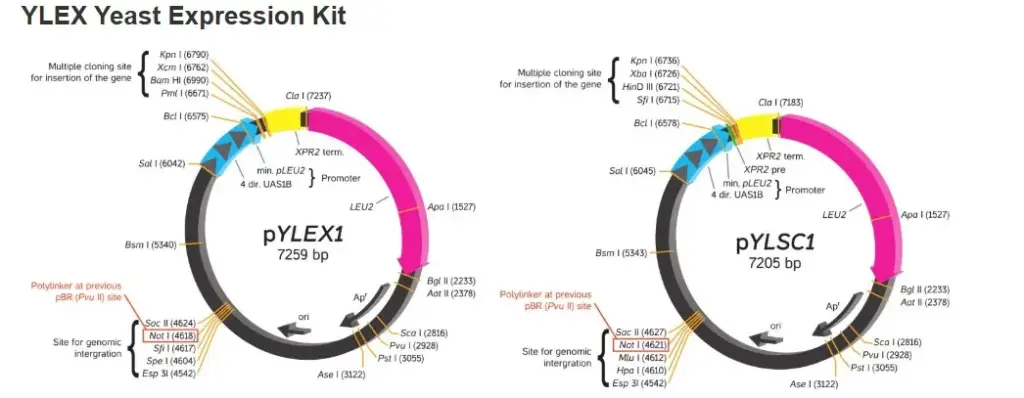
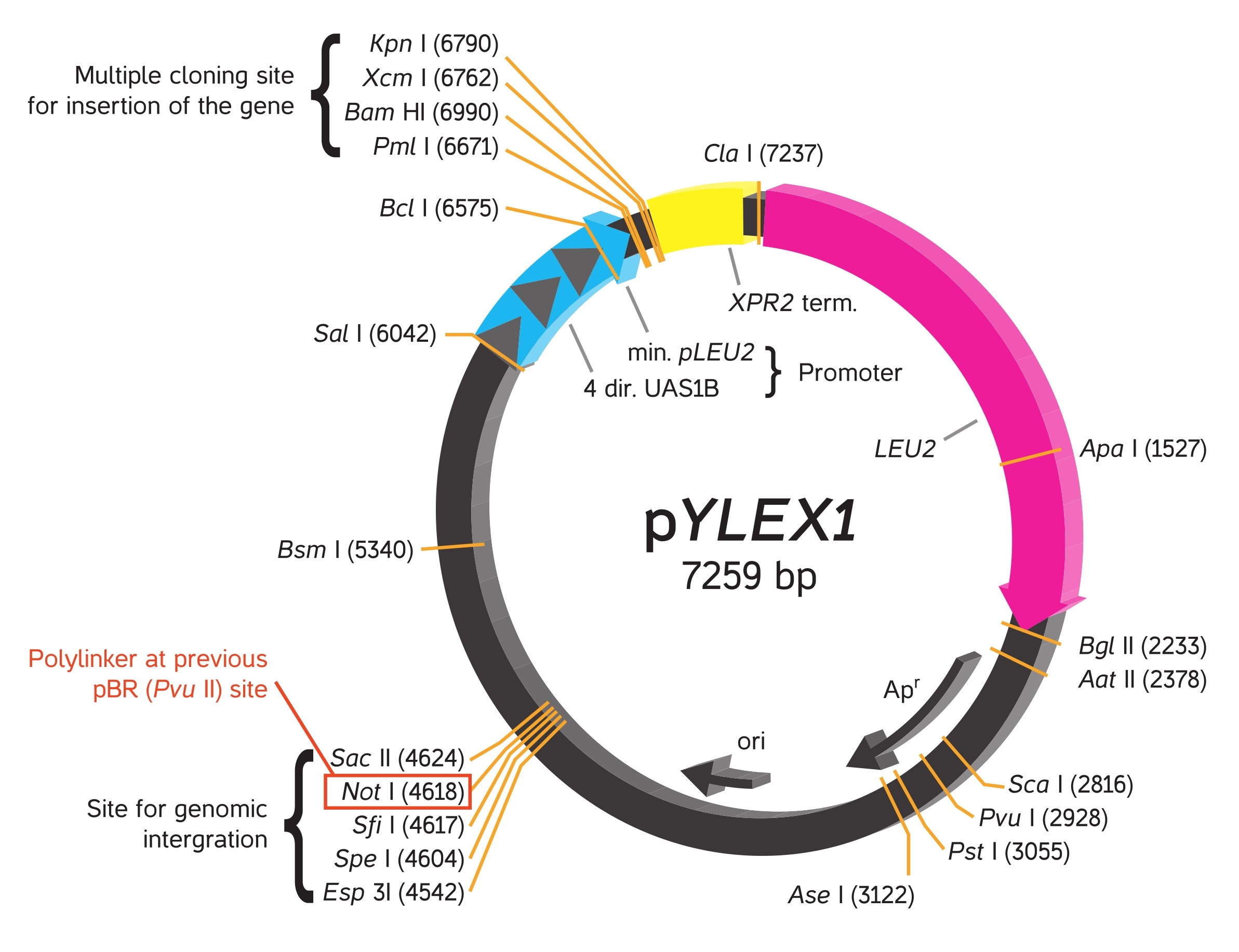
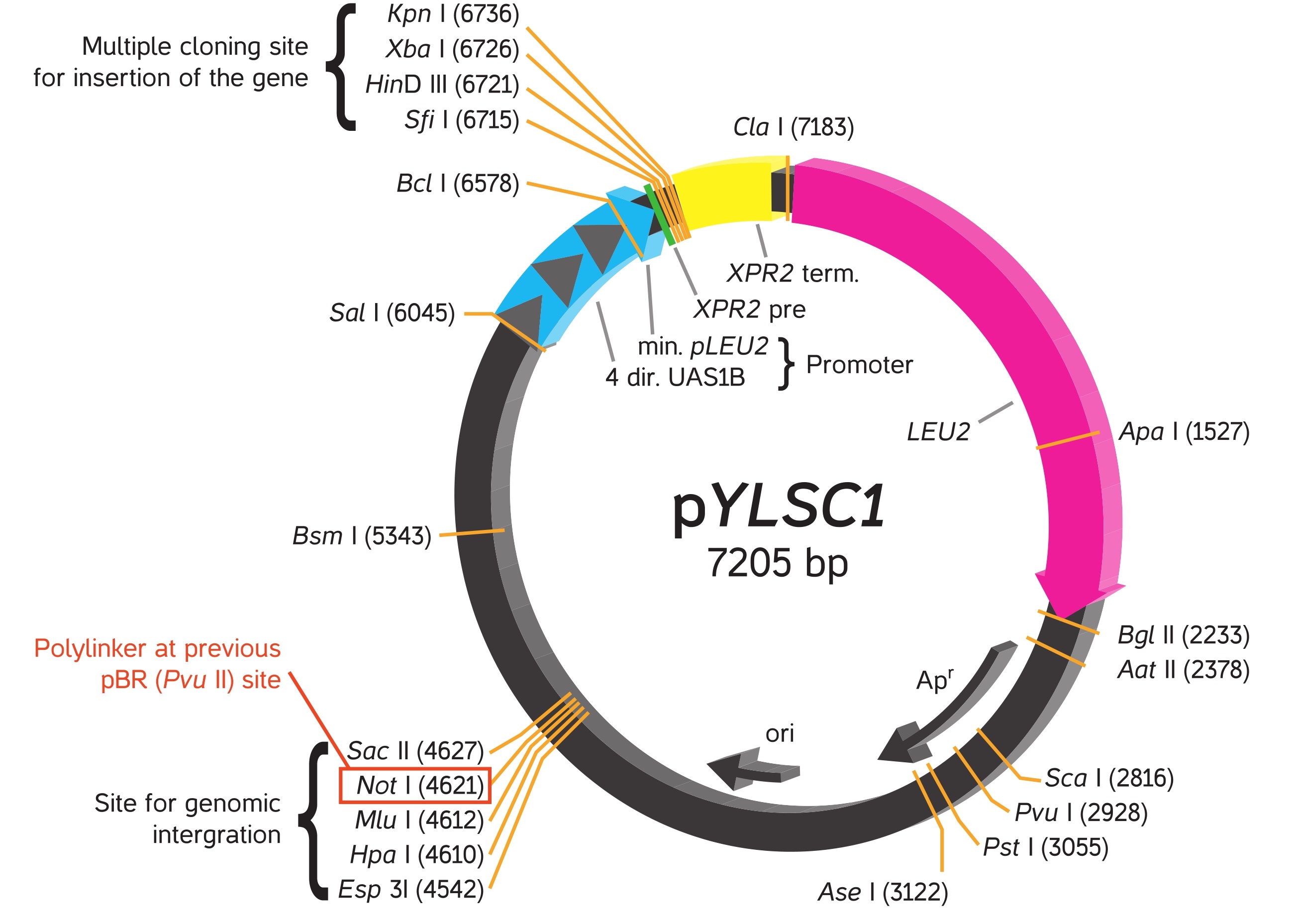
YLEX Expression Kit, based on INRA INAPG licensed patent*, provides an easy approach for cloning and expressing a gene of interest in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Using this kit, heterologous protein may be expressed intracellularly or secreted from the cell into medium by selecting respectively the supplied expression vector pYLEX1 or pYLSC1.
Using YLEX Expression Kit, heterologous protein expression is driven by a strong hybrid promoter (hp4d) carrying four tandem copies of an upstream activator sequence (UAS1B) from pXPR2 and a minimal pLEU2 fragment. To achieve expression in yeast, pYLEX1 containing a cloned gene of interest is linearized by a selected restriction enzyme to produce an expression cassette that can integrate with high efficiency into the Y. lipolytica genome by homologous recombination with an integrated pBR platform. A leucine gene (LEU2) in pYLEX1 provides for selection of yeast containing an integrated expression cassette by allowing their growth on leucine-free minimal medium. The integrated vector is particularly stable, and targeted monocopy integration allows a direct comparison of the properties of the transformants, which are comparable in terms of locus and copy number.
To achieve secretion of protein from yeast cells, the gene of interest is cloned into pYLSC1, downstream from the XPR2 pre region (secretion signal from XPR2 gene), resulting in expression of a secretion signal fusion protein. The XPR2 pre region directs the fusion protein to be eciently transported through the yeast secretory pathway. The secretion signal fusion protein undergoes sequential processing by signal peptidase and protease in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex respectively, resulting in the secretion of the native form of the protein of interest into the culture medium.
Features
- Safe: Y. lipolytica was classified as GRAS (Generally Regarded As Safe) by the US FDA (Food and Drug Administration)
- Simple: a simple tool for expressing heterologous protein
- Easy manipulation: like E. coli and S. cerevisiae
- Stable: strong stability in vectors and constructed plasmids
- Reliable: vectors integrated at the same site in genome
- Flexible: both expression and secretion vector provided (proteins may be expressed intracellularly or be secreted from the cell into medium)
- High growth ability: high secretion capacity & high product yield
- Less protein degraded: no extracellular protease synthesized by a special protease-deficient Yarrowia strain
- Mass production: industrial mass production of recombinant proteins
- Less hyperglycosylation:able to perform post-translational processing of complex proteins, unlike S. cerevisiae
Applications
Technical
Plasmids
Vectors provided in the YLEX contain a strong hybrid promoter carrying four tandem copies of upstream activator sequences (UAS1B) fragment from pXPR2 and a minimal pLEU2 fragment. Unlike the frequently used Yarrowia promoter (pXPR2), this stable hybrid promoter directs protein expression constantly without multiple influences by nutritional and environmental factors in the medium.
When a constructed plasmid with the hybrid promoter followed by a cloned gene of interest is linearized by the selected restriction enzyme, it becomes an expression cassette that can integrate into the Y. lipolytica genome by homologous recombination within the process of transformation. The successful transformants are ready for expression or secretion of recombinant protein depending on whether secretion signal appears on the plasmid. For more information, please read the articles cited in this catalog.
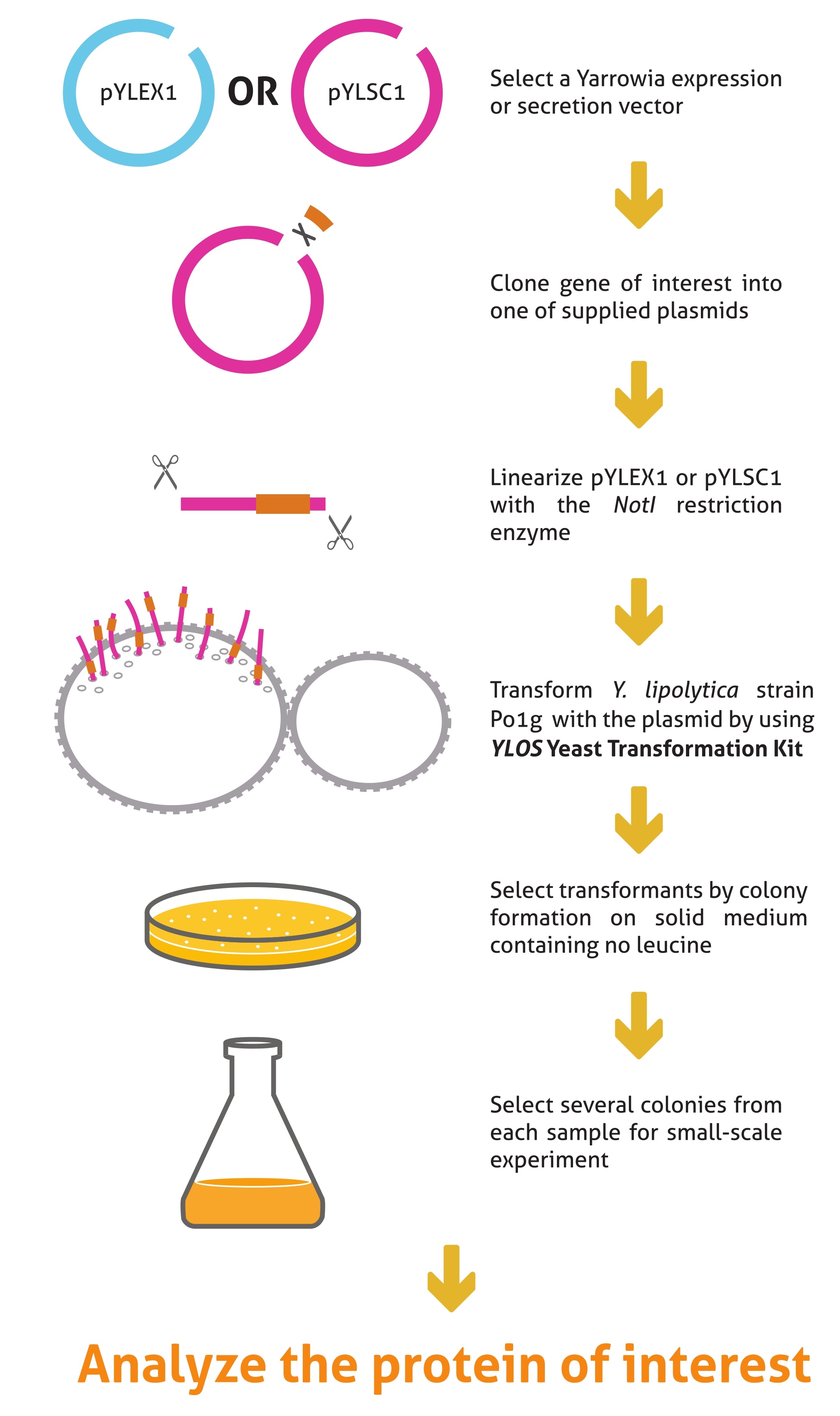
Protocol